Modern CMake快速入门——作为构建系统
文章目录
Basics
|
|
EXCLUDE_FROM_ALL关键字用于禁用子文件夹中targets的默认构建
和系统环境有关的变量 : CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME系统名称, CMAKE_HOST_*, CMAKE_SIZEOF_VOID_P查询32-bit or 64-bit, CMAKE_CXX_BYTE_ORDER系统字节序。[关于交叉编译的官方文档]
查询host系统的特性
|
|
配置工具链
设置C++版本。设置某个target的版本set_property(TARGET <target> PROPERTY CXX_STANDARD <standard>)
修改全局变量设置整个project的版本CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD,该命令不强制使用该版本,需要
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)来强制规定版本
set(CMAKE_CXX_EXTENSIONS OFF)
编译器支持的特性会在configuration stage存放在CMAKE_CXX_
COMPILE_FEATURES 变量中,可用于查看某些特性是否支持
|
|
对版本的支持特性cxx_std_98, cxx_std_11, cxx_std_14, cxx_std_17, cxx_std_20,
and cxx_std_23
运行测试
|
|
Targets
target: 一个逻辑对象,包含属性,描述依赖关系
构建一个target会生成一个artifact(可执行文件或库文件)喂给其他target或作为最终构建结果的一部分
定义target的命令
add_executable(): 定义一二进制targetadd_library(): 定义库targetadd_custom_target(): 定义由某个命令的结构为target。用于计算checksum,收集静态分析报告等
如
|
|
Properties
cmake可以在各个层级控制target(或非target)具有的properties。如set_property(), set_directory_properties(), set_target_properties(), set_source_files_properties()等。
Dependency graph
描述targets之间依赖关系命令
taerget_link_libraries(): 可以控制属性的传播,常用于定义实际的库和可执行文件add_dependencies(): 常用于定于用户自己的顶级target来设置构建顺序
构建系统会从我们定义的顶层targets递归向下构建子target
例如对于以下应用:
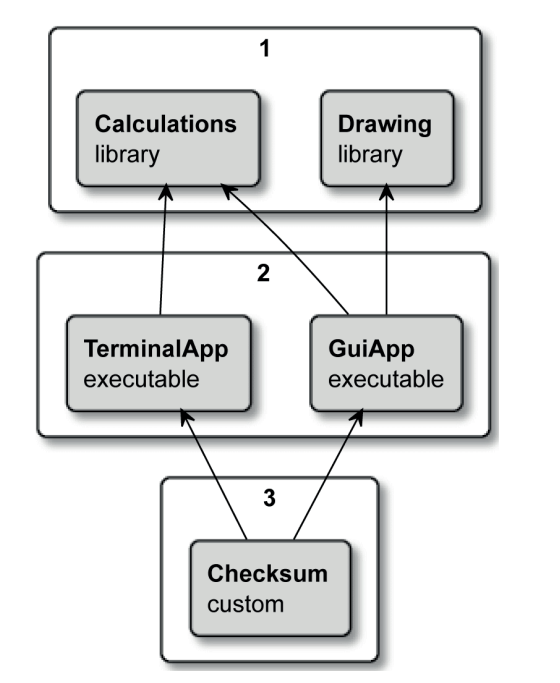
描述如下
|
|
可视化
命令cmake --graphviz=test.dot .生成可视化描述文件,然后用(在线)工具生成图像,如
Graphviz Online (dreampuf.github.io)。
Targets properties
target的一部分属性可以修改,一部分是只读的。读写某个target的属性的命令
|
|
Transitive usage requirements
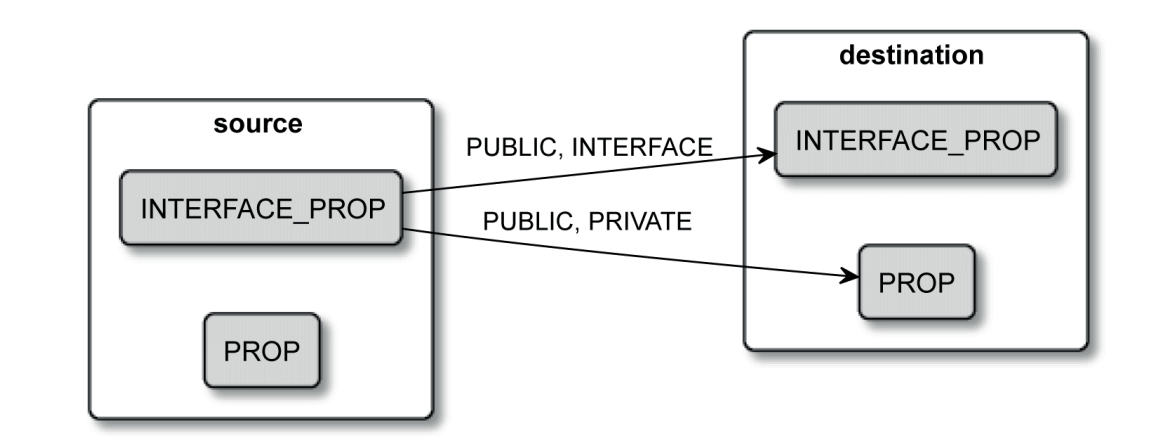
transitive usage requirements即描述有依赖关系的targets,source target(被使用的target)的属性如何传递给destination target(使用其他target)。
set_target_properties(), target_compile_definitions(), target_link_options()等命令中的可见性关键字用于设置属性存储在target中的位置,这决定了source target中的属性(包括头文件搜索路径,编译选项等属性)是否会传递给destination target,其含义如下:
PRIVATEsets the property of the source target.INTERFACEsets the property of the destination targets.PUBLICsets the property of the source and destination targets.
cmake通过特定前缀来区分私有属性(private property)和公有属性(interface property),对于PUBLIC/INTERFACE的属性,其属性名将会有INTERFACE_前缀。在configuration stage中,cmake会将source target中的带有INTERFACE_前缀的属性复制到destination target中。
|
|
而target_link_libraries()命令中的可见性关键字用于设置source target的属性将会被保存到destination target中的什么位置,这决定了属性能传递多远(默认为PUBLIC),其含义如下:
PRIVATEappends the source value to the private property of the destination.INTERFACEappends the source value to the interface property of the destination.PUBLICappends to both properties of the destination.
属性的可见性总结如下图:
解决传播属性的冲突
多个source target可能传递同名属性到一个destination target上,为了解决冲突,我们需要在source target中定义INTERFACE_LIB_VErSION,然后在destination target中选择如下策略处理冲突
COMPATIBLE_INTERFACE_BOOL: 检查传播到target中的属性是否可以求值为同一个bool值COMPATIBLE_INTERFACE_STRING: 检查传播到target中的属性是否可以求值为同一个string值COMPATIBLE_INTERFACE_NUMBER_MAX: 选择传播到target中的最大的属性COMPATIBLE_INTERFACE_NUMBER_MIN: 选择传播到target中的最小的属性
例子
|
|
Pseudo targets
Imported targets
从外部导入的项目中的target的某些属性和传递性也可以被设置
Alias targets
|
|
alias targets的属性是只读的,且无法导出
Interface libraries
- 用于表示header-only库
|
|
- 用于设置属性
|
|
add_custom_command()
as a generator
|
|
|
|
as a target hook
hook点包括:
PRE_BUILDwill run before any other rules for this target (Visual Studio generators only; for others, it behaves like PRE_LINK).PRE_LINKbinds the command to be run just after all sources have been compiled but before the linking (or archiving) the target. It doesn’t work for custom targets.POST_BUILDwill run after all other rules have been executed for this target.
|
|
Generator expressions
generator expressions用于在configuration/generation stage动态求值,格式:
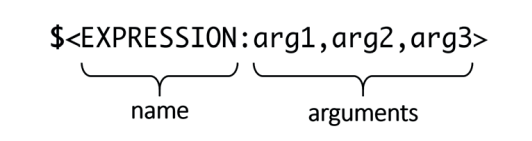
可以嵌套generator expressions或变量,如$<UPPER_CASE:$<PLATFORM_ID>>,$<UPPER_CASE:${my_variable}> 。各种不同作用的generator expression参考[官方文档]。一些例子:
|
|
|
|
编译配置
target_compile_features(): Require a compiler with specific features to compile this target.target_sources(): Add sources to an already defined target. (可用于根据条件添加源文件)target_include_directories(): Set up the preprocessor include paths.target_compile_definitions(): Set up preprocessor definitions.target_compile_options(): Compiler-specific options for the command line.target_precompile_headers(): Optimize the compilation of external headers.
通过设置CMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS变量可以在build目录下生成包含详细编译命令的文件compile_commands.json。
预处理配置
添加头文件的搜索路径
|
|
AFTER|BEFORE用于表示这些路径被添加到 INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES这个属性的前还是后。
添加宏定义
|
|
Configuring the headers
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring the optimizer
使用target_compile_options()为target独立配置或使用作用于所有targets的全局变量CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS_DEBUG, CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS_RELEASE。
Reducing compilation time
Precompilation of headers
|
|
|
|
Unity builds
通过将多个源文件合并作为一个统一的单元编译。注意各个文件之间的名字可能冲突。[官网文档](UNITY_BUILD — CMake 3.24.1 Documentation)
方式:通过set(CMAKE_UNITY_BUILD TRUE)全局配置或逐target配置
|
|
Linking
Type of libraries
add_library(<NAME> STATIC [<source>...]): 创建静态库(a collection of raw object files stored in an archive)add_library(<NAME> SHARED [<source>...]):add_library(<NAME> MODULE [<source>...]): 用于创建运行时作为插件手动加载的动态库,必须使用LoadLibrary()/dlopen()/dlsym()加载。
有关object libraries的传递特性 Oh No! More Modern CMake
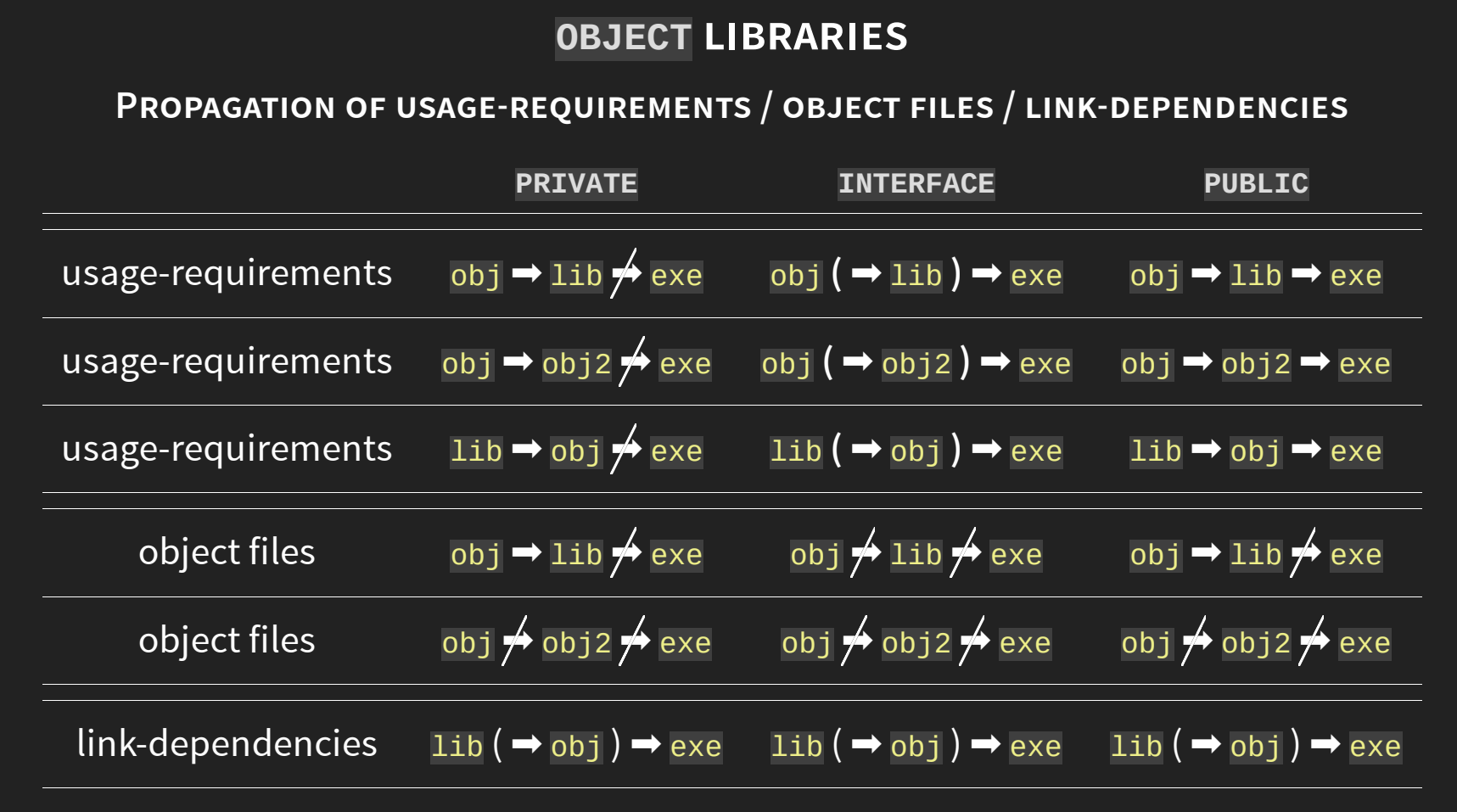
PIC
由target的属性POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODE决定。Shared libraries和modules默认为ON。
管理依赖
find_package()
使用find_package()寻找系统上已安装的包。find_package()通过已有的.cmake脚本(安装cmake后会在<安装目录>/share/cmake-<version>/Modules/目录下存放一些常用包的寻找脚本)根据常用的包管理工具尝试在各种可能的路径下寻找包是否安装。
|
|
|
|
例如在上例中find_package(Protobuf REQUIRED)会通过阈预置的FindProto.cmake脚本取寻找系统上是否安装了Protobuf包。
将局部target提升为全局target(提升后无法取消)。
|
|
ExternalProject
ExternalProject用于配置依赖,对于使用ExternalProject_Add()添加的项目cmake将会执行如下步骤:mkdir-download-update-patch-configure-build-install-test
部分选项如下:
|
|
例子:
|
|
缺点,整个过程是封闭的,我们的项目在构建时无法使用其中的targets。
FetchContent
FetchContent将会在configuration stage将外部项目的target引入主项目中
FetchContent_MakeAvailable()的实际执行过程
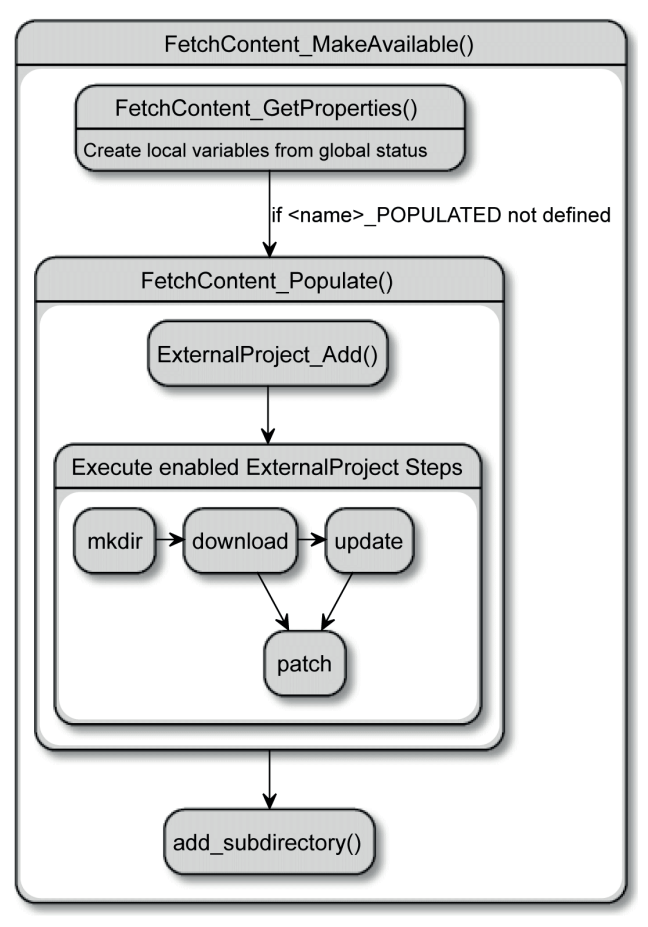
例子:
|
|
安装与打包
导出targets至另一个项目
install()命令将导入一个targets list。
export()命令将targets导出到一个.cmake文件中,这样,另一个项目可以通过include()命令将该.cmake文件包括来导入targets。需要注意这种方式导出的targets使用硬编码的绝对路径进行定位。
|
|
|
|
安装项目
|
|
<options>如下:
- –config : This picks the build configuration for a multi-configuration generator.
- –component : This limits the installation to the given component.
- –default-directory-permissions : This sets the default permissions for the installed directories (in format).
- –prefix : This specifies the non-default installation path (stored in the CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX variable). It defaults to /usr/local for Unix-like systems and c:/Program Files/${PROJECT_NAME} for Windows.
- -v, –verbose: This makes the output verbose (this can also be achieved by setting the VERBOSE environment variable).
文章作者 bobh
上次更新 2022-05-01